Category of Content
Siting Experience Documents Only
Publication Date
Subject Matter
Keywords
M4SF-19ID020303045- Atlas Railcar Phase 3 Final Report
M4SF-19ID020303045- Atlas Railcar Phase 3 Final Report
Nuclear Fuels Storage and Transportation Planning Project Inventory Basis?, Rev 1
Nuclear Fuels Storage and Transportation Planning Project Inventory Basis?, Rev 1
Performance Specification for Standardized Transportation, Aging, and Disposal Canister Systems
Performance Specification for Standardized Transportation, Aging, and Disposal Canister Systems
Appendix B – Revised Railcar-to-Cradle Attachment Interface
Appendix B – Revised Railcar-to-Cradle Attachment Interface
Appendix D – Revised Conceptual Cradle Design Family 4
Appendix D – Revised Conceptual Cradle Design Family 4
Standardized Transportation, Aging, and Disposal Canister Feasibility Study
Standardized Transportation, Aging, and Disposal Canister Feasibility Study
Dry Storage Cask Inventory Assessment
Dry Storage Cask Inventory Assessment
The Social and Ethical Aspects of Nuclear Waste
The Social and Ethical Aspects of Nuclear Waste
Nuclear waste management seems to exist in a perpetual state of crises. For 50 years the nuclear states of the world have fought, and generally lost, the battle to deal with the nuclear waste problem. Worldwide, there is a growing acknowledgement within industry and government that social and ethical issues are just as important as technical issues when developing safe programs for nuclear waste management. This paper is a review of some of the outstanding social and ethical issues that are influencing discussions on nuclear waste management around the world.
U.S. Nuclear Plant Shutdowns, State Interventions, and Policy Concerns
U.S. Nuclear Plant Shutdowns, State Interventions, and Policy Concerns
The United States has the largest nuclear power plant fleet in the world, with 93 reactors that can generate approximately 95,522 megawatts (MW) of electricity. Nuclear power has accounted for about 20% of annual U.S. electricity generation since the late 1980s; in 2020 it was 19.7%. However, the U.S. nuclear power industry in recent years has been facing economic and financial challenges, particularly plants located in competitive power markets where natural gas and renewable power generators influence wholesale electricity prices. Twelve U.S.
Survey of National Programs for Managing High-Level Radioactive Waste and Spent Nuclear Fuel: 2022 Update
Survey of National Programs for Managing High-Level Radioactive Waste and Spent Nuclear Fuel: 2022 Update
In October 2009, the U.S. Nuclear Waste Technical Review Board (Board or NWTRB) published Survey of National Programs for Managing High-Level Radioactive Waste and Spent Nuclear Fuel. For each of the 13 national programs studied, the report catalogued 15 institutional arrangements that had been set in place and 15 technical approaches that had been taken to design repository systems for the long-term management of high-activity radioactive waste.
Going the Distance? The Safe Transport of Spent Nuclear Fuel and High-Level Radioactive Waste in the United States - Summary
Going the Distance? The Safe Transport of Spent Nuclear Fuel and High-Level Radioactive Waste in the United States - Summary
This new report from the National Research Council’s Nuclear and Radiation Studies Board (NRSB) and the Transportation Research Board reviews the risks and technical and societal concerns for the transport of spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste in the United States. Shipments are expected to increase as the U.S. Department of Energy opens a repository for spent fuel and high-level waste at Yucca Mountain, and the commercial nuclear industry considers constructing a facility in Utah for temporary storage of spent fuel from some of its nuclear waste plants.
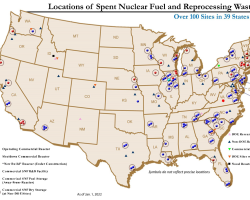
Spent Nuclear Fuel and Reprocessing Waste Inventory, Revision 9
Spent Nuclear Fuel and Reprocessing Waste Inventory, Revision 9
This report provides information on the inventory of spent nuclear fuel (SNF) in the United States located at Nuclear Power Reactor and Independent Spent Fuel Storage Installation sites, as well as SNF and reprocessing waste located at U.S. Department of Energy sites and other research and development centers as of the end of calendar year 2021.
Status and Trends in Spent Fuel and Radioactive Waste Management
Status and Trends in Spent Fuel and Radioactive Waste Management
Status and Trends in Spent Fuel and Radioactive Waste Management is a collaborative project between the IAEA, the European Commission and the OECD Nuclear Energy Agency, with the participation of nuclear industry organization the World Nuclear Association, that aims to consolidate and complement the information gathered from different initiatives around the world.
Dry Storage Cask Inventory Assessment, Revision 2
Dry Storage Cask Inventory Assessment, Revision 2
The report, Commercial Spent Nuclear Fuel and High-Level Radioactive Waste Inventory Report(FCRDNFST- 2013-000263, Rev.4), provides information on the inventory of commercial spent fuel, referred to in this report as used nuclear fuel (UNF), as well as Government-owned UNF and High Level Waste (HLW) in the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) complex. Inventory forecasts for commercial UNF were made for a few selected scenarios of future commercial nuclear power generation involving the existing reactor fleet including one scenario involving reactors under construction.
Transportation Institutional Issues Involving the U.S. Department of Energy's Civilian Radioactive Waste Management Program: The Post Yucca Mountain Years
Transportation Institutional Issues Involving the U.S. Department of Energy's Civilian Radioactive Waste Management Program: The Post Yucca Mountain Years
This 10th anniversary update to the original archive adds several sections that cover relevant topics since 2010. Some of the new topics include the Blue Ribbon Commission on America's Nuclear Future, consent-based siting, tribal engagement, shutdown site visits, and industry interests. Much like the first publication, the purpose of this update is to make it easier for new personnel to learn about what came before them in the hope that this knowledge gives them a greater chance of success.